-
Publish Your Research/Review Articles in our High Quality Journal for just USD $99*+Taxes( *T&C Apply)
Offer Ends On
Hossein Assarzadeh, Malihe Karrabi1* and Seyedeh Fatemeh Namdar
Corresponding Author: Malihe Karrabi, Department of Oral and Prosthodontics, School of Medicine, Sabzevar University of Medical Sciences, Sabzevar, Iran
Received: July 05, 2022 ; Revised: July 11, 2022 ; Accepted: July 14, 2022 ; Available Online: August 31, 2022
Citation: Assarzadeh H, Karrabi M & Namdar SF (2022) Effect of 2% Chlorhexidine and 5% NaOCl as Dentin Rewetting Agents and Ethanol or Acetone-Based Adhesives on Dentin Microtensile Bond Strength. J Oral Health Dent Res, 2(2): 1-9.
Copyrights: ©2022 Assarzadeh H, Karrabi M & Namdar SF. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Views & Citations
Likes & Shares
Abstract
Statement of the Problem: preventing hydrolysis of the hybrid layer and maintaining the resin-dentin interface is a key issue in the success of composite restorations.
Purpose: This study aimed to compare the effects of 2% chlorhexidine (CHX) and 5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) as rewetting agent on resin-dentin microtensile bond strength (MTBS) created by acetone- and ethanol-based adhesives after 6 months.
Materials and Method: In this in vitro study 90 extracted premolars were divided into 3groups (n=30). Mid-coronal dentin was etched and rinsed. In groups 1 and 2, dentin surface was rinsed and gently dried, then 2% CHX and 5% NaOCl were used as rewetting agents, respectively. In group 3, only the excess moisture of dentin surface was removed by a cotton pellet without drying. Each group was divided into two subgroups (n=15). Single Bond adhesive was used in subgroup 1 and Prime & Bond NT in subgroup 2. Samples were restored with Filtek Z250. The teeth were then sectioned to obtain sticks with a cross-sectional area of 1 mm2. The tests were carried out in a microtensile apparatus at a crosshead speed of 1 mm/min after 6 months of storage at 37°C in water. Mean bond strengths were analyzed using the two way ANOVA test and post-hoc multiple comparisons according to the Duncan test at the 0.05 level of significance.
Results: µTBS in CHX group was significantly higher than other groups (p<0.001).in sup groups, Maximum and minimum bond strength was noted in CHX- ethanol group (83.30 MPa) and NaOCl- acetone group (47.46 MPa), respectively.
Conclusion: The combination use of CHX as rewetting agent and an ethanol based adhesive preserve hybrid layer and bond strength over time.
Keywords: Tensile strength, Chlorhexidine, Sodium hypochlorite, Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors, Dental bonding
INTRODUCTION
The main mechanism of resin-dentin bonding is micro-mechanical interlocking of resin in the hybrid layer [1]. Despite the advancement in adhesive dentistry, there are some concern about optimal resin infiltration into etched collagen fibrils in total etch technique. Incoherence in depth of etched dentin and adhesive resin penetration is a challenge for clinicians in this technique [2]. It causes the Water retention in deep layers, acceleration in hybrid layer hydrolysis, degeneration of hydrophilic polymers of the adhesive system and finally gap formation between the restoration and tooth structure [3] that leads to bond strength decrement in 100 days to 6 months after the restoration [4].
Two major factors initiate the hybrid layer degeneration including:
Indeed, Dentin matrix has endogenous proteolytic activity, which is related to the collagenolytic/ gelatinolytic function of MMPs [7]. This Proteases deposit in dentin structure during its mineralization phase and firmly bond to collagen fibrils. In normal conditions, MMPs are in the form of inactive proenzymes in the ECM, but are activated in certain circumstances such as low PH [8]. This enzymatic degradation of collagen matrix by the host-derived enzymes plays an important role in degradation of the hybrid layer over the time [9].
Several new therapeutic strategies have been suggested to limit or inhibit the biodegradation of this layer such as:
MMPs within the dentin matrix require calcium to maintain their tertiary structure and require zinc for their hydrolase activity. Thus, these enzymes can be inactivated by using divalent cation chelators on etched dentin surface [12]. In this process, MMP inhibitors chelate the calcium ion or replace the zinc ion on the active site and break-down the pro-peptide molecules of MMPs. Alternatively, they limit or inhibit their access and activity by coating the substrate [13].
CHX is the most commonly used MMP inhibitor that can inhibit the activity of MMPs [14]. Its mechanism of action is through its calcium chelating effect [13]. It has been claimed that chlorine behaves like an amphiphilic molecule that can bind to zinc of the catalytic domain of MMP, preventing its hydrolytic activity [15].
Furthermore, evidence shows that removal of naked collagen fibrils from the etched dentin surface prior to the application of adhesive resin in total etch technique, by deproteinizing agents, can prevent their degradation. It removes the organic compounds and parts of the exposed collagen without mineral support [16]. In this regard, NaOCl is a well-known non-specific proteolytic agent that can remove organic materials and helps to more effective resin penetration [17,18].
Another factor that can affect the resin-dentin bond durability is adhesive capability in penetration into deep parts of etched tubules. This ability mainly depends on adhesive solvent type. Acetone with a boiling temperature of 56.58°C and ethanol with a boiling temperature of 78.38°C are the most commonly used solvents in dental adhesives [19,20]. They are used in the composition of adhesives for removal of excess water and re-expanding the collapsed collagen network [21,22]. In presence of excessive moisture, water decreases the inter-fibrillar space, and limits resin infiltration around exposed collagen fibrils [23]. Hence not resin covered fibrils are susceptible to enzymatic hydrolysis and degradation by MMPs, removing the excess water without over-drying of dentin surface is highly important [24]. Also residual water permits water permeation through the bonded interface even after polymerization [25]. So adhesive solvent type and its ability in excess water removal is a key factor in strength and durability of resin-dentin bond [20,26].
Some studies have evaluated the effect of different rewetting agent (CHX or NaOCl) on bond strength of resin- dentin, separately, and have reported contradictory results [9-11,16,27,28]. The discrepancies between the results of different studies might be attributed to differences in adhesive solvent type, application mood and time of rewetting agent and storage time. Few studies have been done on comparison between these two rewetting agent, So that the effect of adhesive solvent type in composition with these agents is equivocal. Therefore the need for a comprehensive study taking into account the above factors in this area is felt.
So, the aim of present study is to assess the effects of 2% chlorhexidine and 5% NaOCl as dentin rewetting agents on resin-dentin microtensile bond strength (MTBS) created by ethanol-based or acetone-based adhesives after 6 months. The null hypotheses of this study were (I) application of CHX and NaOCl would not preserve the bond strength over time, and (II) type of solvent would have no effect on resin-dentin MTBS.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This in vitro, experimental study evaluated 90 extracted caries-free human first premolars extracted because of orthodontic treatment. The teeth were disinfected with 0.5% chloramine T solution and stored in distilled water. A flat surface of midcoronal dentin was exposed using water-cooled diamond disc and a cutting machine (Labcut 1010; Extec Co., Enfield, CT, USA). A standardized smear layer was created on the surface by wet-sanding with 600-grit sandpaper for 60s. The teeth were then randomly divided into three groups (n=30). In all three groups, dentin surface was etched with 37% phosphoric acid (Fine Etch Spident, Korea) for 15 s and rinsed with water for 15 s. In groups 1 and 2, moisture was removed from the dentin surface using gentle air spray.
In group 1, 2% CHX (consepsis ultra Inc., south Jordan, USA) was used for dentin rewetting for 60 s [29]. In group 2, 5% NaOCl (Fischer Scientific, Hampton, NH) was used for dentin rewetting for 120 s (16). In group 3, excess water was removed but some moisture remained on the surface (control group). Next, all teeth were randomly divided into 2 subgroups (n=15) and the two bonding agents were applied. In subgroup 1, Single Bond with ethanol solvent (3M ESPE, USA) and in subgroup 2, Prime & Bond NT (Dentsply, DeTrey, Konstanz, Germany) with acetone solvent were used according to the manufacturers’ instructions. Next, the bonding agent was cured with a LED curing unit (Degolux II; Degussa AG, Gschattsbereich Dental, D-63457 hanau Wolfgang, Germany) with a light intensity of 800 mW/cm2 for 10 s according to Instructions for use (Table 1 presents the adhesive contents and Instructions for use). The crowns of the flattened teeth were then reconstructed with three 1.5mm-layers of a hybrid resin composite (Filtek Z250) each layer being light-cured for 40 s with a light curing unit (Figure 1).

Sample preparation for MTBS test and storage
The samples in each group were sectioned longitudinally perpendicular to the resin-dentin interface using a diamond saw (Isomet 1000 Precision Saw, Buehler Ltd., Lake Bluff, IL, USA), resulting in 45 sticks with a cross-sectional area of 1 mm2 and 8.5mm height. The samples were stored in saline for 6 months. The saline was refreshed once a week to prevent contamination. No preservative or antibacterial agent was used.
After 6 months of storage, the sticks were mounted in a jig with a special cyanoacrylate glue and tested using a universal testing machine ((SD Mechatronik MTD-500/Germany). Tensile load was applied at a crosshead speed of 1 mm/min with 10 mm deflection and maximum force of 100 N until failure.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 16.0 for Windows. The values were normally distributed with Shapiro-Wilk test, therefore Two-way ANOVA was used to compute differences between dependent groups. Also Duncan test was applied for post-hoc multiple comparisons at the 0.05 level of significance.
RESULTS
The means and standard deviations of the bond strength values are shown in Table 2. As shown, a significant difference was noted in MTBS of the groups based on rewetting agent (p=0.044). However, the effect of type of adhesive solvent was not significant (p=0.077). Also interaction effect of rewetting agent and the type of adhesive solvent significantly affected the MTBS (P=0.045).
No significant difference was detected between NaOCl and water subgroups by two way ANOVA set at α=0.05.
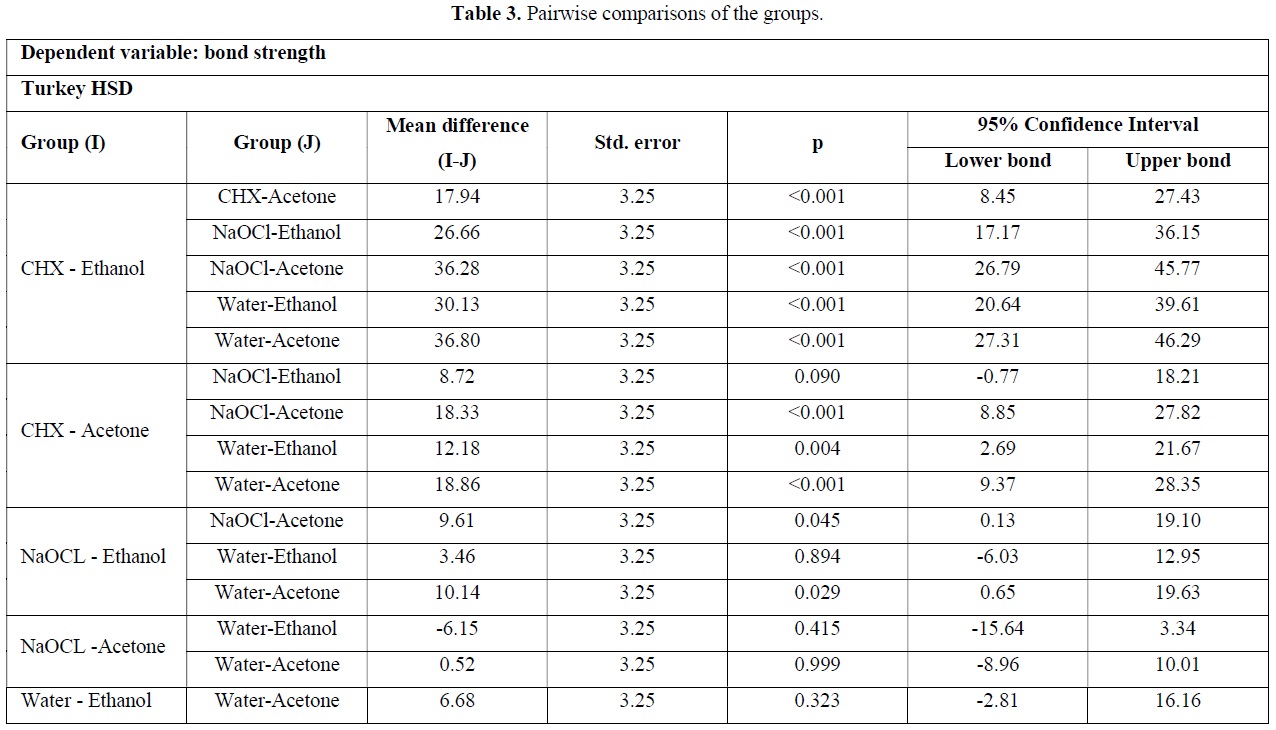
Table 3 presents pairwise comparing each group with all other ones. Based on this data, there was a significant difference between CHX/ethanol group with CHX-Acetone, NaOCl-Ethanol, NaOCl-Acetone, Water-Ethanol and Water-Acetone groups (p<0.001). Also the difference between CHX-Acetone group with Water-Acetone and NaOCl-Acetone groups was significant (p<0.001). Pairwise comparisons between other groups was not significant and minimum difference was noted between CHX-acetone and NaOCl-ethanol groups (P=0.090).

DISCUSSION
According to the results of the present study, Application of 2% CHX on etched dentin surface for 60 s preserved the bond strength over time while use of 5% NaOCl had no significant effect on resin-dentin bond strength in comparison with control group (water). Also there was no significant difference between ethanol-based adhesive compared with acetone-based adhesive with regard to preserving the resin-dentin bond strength. Therefore, the first of the study was rejected while the second hypothesis was confirmed. It seems that these results are related to these materials’s influence in hybridization process. In this process, acid-etching removes the hydroxyapatite, exposes the collagen fibrils and creates a naked collagen network. This leads to resin penetration and formation of a hybrid layer and creating micromechanical retention [1,30]. Hybridization process requires a vehicle to remove the excess water and at the same time, transfer the polymerizable monomers into open tubules and microscopic spaces in-between the collagen fibrils [21,31].
It is noticeable that the lack of complete removal of water and incomplete penetration of the resin into collagen inter-fibrillar space predispose this layer to hydrolytic degeneration of resin monomers and collagen fibrils in aqueous environment after 6 months to 3 to 5 years [32,33].
This degeneration occurs for two reasons:
Endogenous MMPs enzymes have been claimed to play a role in secretion of dentin growth factors and deposition of peritubular and tertiary dentin [36]. In fact, dentin MMPs gradually change the structure and mechanical properties of mineralized dentin during physiological and pathological processes [37].
MMPs are divided into different types based on their activity such as gelatinases (MMP-2 and -9), collagenase (MMP-8) and stromelysin (MMP-3) [8,13]. Collagenolytic enzymes play a role in formation of peritubular and tertiary dentin and pulp defense responses [38]. MMP-8 is mainly responsible for hydrolysis of type I collagen fibrils while MMP-9 is responsible for gelatinolytic activities within the carious dentin [8]. MMP-2 present in coronal dentin and its maximum concentration can be found at 9-10 µm from the dentino-enamel junction and 90-200 µm around the pre-dentin [39]. Collagen is mainly degenerated by the activity of MMP-8 (collagenase) while more degeneration is performed by MMP-2 and MMP-9, which are gelatinizes. Conversion of insoluble collagen to soluble peptides by the activity of MMPs leads to destruction of the hybrid layer and loss of micromechanical retention of the hybrid layer, which eventually lead to a significant reduction in resin-dentin bond strength [35].
Thus, MMP inhibitors are used to treat the dentin surface and inhibit this mechanism. Although the exact mechanism of MMP inhibitors has not been fully elucidated, the most commonly accepted theory regarding their mechanism of action is divalent chelation of metal ions especially calcium and zinc ions. Thus, they must have functional groups to chelate the zinc ion of catalytic domain. This inhibitors limit the binding of MMPs to the collagen substrate and prevent the formation of cleavage and cracks and subsequent failure [40,41].
CHX is the most commonly used MMP inhibitor which can inhibit MMP-2, MMP-8 and MMP-9, even in low concentrations, due to its Zn2+ cation chelating property [42].
It that can be used in three different modes:
Pretreatment of etched dentin surface with CHX (method I), Also, increases micromechanical interlocking between resin and dentin and subsequent formation of a better hybrid network and increased inter-fibrillary spaces, which enhance adhesive resin penetration [44]. This leads to formation of a hybrid layer with higher quality that preserves the bond strength over time [45]. The result of present study showed that treatment of etched dentin surface with 2% CHX improved bond strength in combination with two adhesive types that were in line with those of other studies that showed that use of CHX inhibited the degradation of the hybrid layer over time [46-49].
On the other hand, Use of deproteinizing agents such as NaOCl has also been suggested for removal of the exposed collagen and prevention of its subsequent degradation. Application of this agent on the surface of etched dentin, removes the naked collagen fibrils and exposes the labyrinths of lateral secondary tubules witch not normally seen in etched dentin [50]. Also, it exposes the network of secondary lateral canals on superficial dentin and widens the deep dentinal tubules, resulting in formation of longer resin tags [16,50]. Finally, removal of organic materials increases dentin surface wettability and roughness, so improve resin penetration [51]. This increases chemical bonds between the primer and deproteinized dentin surface that leads to better distribution of adhesive agent on the surface [52]. It has been claimed that application of adhesive resin on demineralized dentin treated with NaOCl acts similar to the application of adhesive resin on the etched enamel because this substrate has less minerals, is rougher and more irregular, and its surface has non-homogenous porosities [51,53].
Nonetheless, in such conditions, failure in removing the water remained in deep areas would lead to formation of a weak polymer network. Besides that, NaOCl has anti-oxidative effect along with its deproteinizing property and generates superoxide radicals in aqueous environments. Presence of such free radicals in demineralized dentin treated with NaOCl can compete with the propagating free radicals of vinyl during the light-curing process of adhesive. This would lead to premature chain termination and incomplete polymerization of adhesive [54,55]. This material also results in the formation of amino-acid-derived chloramines and hypochlorous acid that have been shown to increase the proteolytic susceptibility of these collagen proteins [28].
It seems that interaction of above factors resulted in absence of a significant difference between the bond strength of this group and the control group in combination with two adhesives. The current results confirmed previous findings regarding no significant effect of NaOCl application on demineralized dentin on bond strength [11,16,49,56].
The results also indicate that although adhesive solvent type has not a significant effect on the bond strength, but the composition of solvent type and rewetting agent significantly affect it. So that in this study CHX/ethanol group yielded maximum bond strength while lower bond strength was observed in Water/acetone and NaOCl/acetone groups.
This may be due to the interaction between mentioned factors during resin-dentin hybridization. An optimal resin-dentin bond is obtained by complete elimination of water entrapped in deep parts of etched dentin and optimum infiltration of adhesive monomers into etched dentinal tubules [57]. Failure in complete water removal leads to incomplete resin penetration, formation of an imperfect polymer chain, which is weak and susceptible to water sorption, resin leaching, hydrolysis and nano-leakage. While Enhanced resin penetration into the collagen network decreases water sorption and aging, and prevents the break-down of collagen network [35,42].
After dentin demineralization by acid etching, the collagen fibrils are bonded to each other via the intra-fibrillar hydrogen bonds, and high-viscosity adhesives cannot well penetrate into the entire depth of demineralized acid-etched dentin [58]. Therefore, it is imperative to mix high-viscosity monomers with a highly volatile solvent to increase the penetration depth of resin into demineralized dentin [56,59]. In fact, an ideal solvent should optimally decrease the viscosity and enhance the bond strength between hydrophobic and hydrophilic components present in the hybrid layer [60]. Volatile acetone and ethanol solvents are added to adhesives to serve this purpose. These solvents enhance the bonding of hydrophobic and hydrophilic components and prevent phase separation of adhesive components. They also remove water from deep areas of demineralized dentin, which would enhance better penetration of resin monomers into porosities between the collagen fibrils and improve micro-retention in dental substrate [61,62]. Studies have been shown that ethanol in addition to higher vapor pressure and water- chasing properties can denature MMPs [35]. This denaturation and inhibition of enzyme activity can reinforce the effect of CHX in inhibiting the MMPs enzymes. Thus, combination of CHX and ethanol has a greater effect on MMPs inhibition that can enhances the efficacy of the bond and leads to higher bond strength [46]. While, acetone is more sensitive to moisture than ethanol and with having lower vapor pressure, has lower potential for water chasing and re-expansion of collapsed collagen fibrils for better resin penetration [46,63]. So when using NaOCl in combination with acetone-based adhesives, due to the entrapment of water in deeper areas and the inadequacy of acetone in extracting water from these areas [63], the bond strength decrease significantly. Therefore, the combined effect of rewetting agent and adhesive solvent type, play an important role in the strength and durability of the bond. As in this study, maximum bond strength was observed in CHX/ethanol group (may be because of their MMP inhibition property) and lower bond strength was observed in Water/acetone and NaOCl/acetone groups (Probably due to incomplete water removal from deep dentin area).
The effect of rewetting agents used in the present study, independently and without considering the type of solvent, has been investigated in previous studies [11,16,46-48,45].
In the present study, it was tried to compare the effect of these agents, considering the adhesives solvent types, simultaneously, in a more comprehensive study.
However, despite considering the above in the present study, there are still some limitations in this study that can be overcome in future studies by considering the large sample size, more adhesive type and the use of load cycling or thermos-cycling.
Also today, with the development in adhesives dentistry and more use of one-step adhesive containing different solvent type, the need for similar studies in this field is felt.
CONCLUSION
The current results showed that:
Combined use of CHX as dentin rewetting agent and ethanol-based adhesive had additive effect on inhibition of MMPs enzymes which resulted in significantly higher preservation of bond strength compared with other groups over the time.
REFERENCES
No Files Found
Share Your Publication :